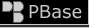





 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
In the photo in the upper left corner you can see the USS LCS122, LT Richard MCCool, Commanding Officer. Along with the USS LCS86, the two 159 foot vessels made it
alongside the sinking destroyer and were able to remove her crew to safety. To my knowledge this is the only sinking of a U.S. Navy ship during combat without loss of life.
On June 11th, the USS LCS122 would take a direct "Kamikaze" hit just below her conning tower. LT McCool would receive the Congressional Medal of Honor
for his heroic action on those two days in June 1945. McCool remained on active duty, retiring from the U.S. Navy in 1974 having acheived the rank of Captain.
Here is a story that I recevied via e-mail on the history of the William D. Porter:
From November 1943, until her demise in June 1945, the American destroyer 'William Porter' was often hailed - whenever she entered port or joined other Naval ships - with the greetings: 'Don't shoot, we're Republicans!' For a half a century, the US Navy kept a lid on the details of the incident that prompted this salutation. A Miami news reporter made the first public disclosure in 1958 after he stumbled upon the truth while covering a reunion of the destroyer's crew. The Pentagon reluctantly and tersely confirmed his story, but only a mattering of newspapers took notice.
Fifty years ago, the Willie D as the Porter was nicknamed, accidentally fired a live torpedo at the battleship Iowa during a practice exercise. As if this weren't bad enough, the Iowa was carrying President Franklin D. Roosevelt at the time, along with Secretary of State, Cordell Hull, and all of the country's W.W.II military brass. They were headed for the Big Three Conference in Tehran, where Roosevelt was to meet Stalin and Churchill. Had the Porter's torpedo struck the Iowa at the aiming point, the last 50 years of world history might have been quite different.
The USS William D Porter (DD-579) was one of hundreds of assembly line destroyers built during the war. They mounted several heavy and light guns, but their main armament consisted of 10 fast-running and accurate torpedoes that carried 500-pound warheads. This destroyer was placed in commission on July 1943 under the command of Wilfred Walker, a man on the Navy's fast career track. In the months before she was detailed to accompany the Iowa across the Atlantic in November 1943, the Porter and her crew learned their trade, experiencing the normal problems that always beset a new ship and a novice crew. The mishaps grew more serious when she became an escort for the pride of the fleet, the big new battleship Iowa.
The night before they left Norfolk, bound for North Africa, the Porter accidentally damaged a nearby sister ship when she backed down along the other ship's side and her anchor tore down her railings, life rafts, ship's boat and various other formerly valuable pieces of equipment. The Willie D merely had a scraped anchor, but her career of mayhem and mishaps had begun.
Just twenty four hours later, the four-ship convoy consisting of Iowa and her secret passengers and two other destroyers was under strict instructions to maintain complete radio silence. As they were going through a known U-boat feeding ground, speed and silence were the best defense. Suddenly, a tremendous explosion rocked the convoy. All of the ships commenced anti-submarine maneuvers. This continued until the Porter sheepishly admitted that one of her depth charges had fallen off her stern and exploded. The 'safety' had not been set as instructed. Captain Walker was watching his fast track career become side-tracked. Shortly thereafter, a freak wave inundated the ship, stripping away everything that wasn't lashed down. A man was washed overboard and never found. Next, the fire room lost power in one of its boilers. The Captain, by this point, was making reports almost hourly to the Iowa on the Willie D's difficulties. It would have been merciful if the force commander had detached the hard luck ship and sent her back to Norfolk. But, no, she sailed on.
The morning of 14 November 1943 dawned with a moderate sea and pleasant weather. The Iowa and her escorts were just east of Bermuda, and the president and his guests wanted to see how the big ship could defend herself against an air attack. So, Iowa launched a number of weather balloons to use as anti-aircraft targets. It was exciting to see more than 100 guns shooting at the balloons, and the President was proud of his Navy. Just as proud was Admiral Ernest J King, the Chief of Naval Operations; large in size and by demeanor, a true monarch of the sea. Disagreeing with him meant the end of a naval career. Up to this time, no one knew what firing a torpedo at him would mean. Over on the Willie D, Captain Walker watched the fireworks display with admiration and envy. Thinking about career redemption and breaking the hard luck spell, the Captain sent his impatient crew to battle stations. They began to shoot down the balloons the Iowa had missed as they drifted into the Porter's vicinity.
Down on the torpedo mounts, the crew watched, waiting to take some practice shots of their own on the big battleship, which, even though 6,000 yards away, seemed to blot out the horizon. Lawton Dawson and Tony Fazio were among those responsible for the torpedoes. Part of their job involved ensuring that the primers were installed during actual combat and removed during practice. Once a primer was installed, on a command to fire, it would explode shooting the torpedo out of its tube.
Dawson, on this particular morning, unfortunately had forgotten to remove the primer from torpedo tube #3. Up on the bridge, a new torpedo officer, unaware of the danger, ordered a simulated firing. "Fire 1, Fire 2," and finally, "Fire 3." There was no fire 4 as the sequence was interrupted by an unmistakable whooooooshhhhing sound made by a successfully launched and armed torpedo. Lt H. Steward Lewis, who witnessed the entire event, later described the next few minutes as what hell would look like if it ever broke loose.
Just after he saw the torpedo hit water on its way to the Iowa and some of the most prominent figures in world history, Lewis innocently asked the Captain, 'Did you give permission to fire a torpedo?' Captain Walker's reply will not ring down through naval history... although words to the effect of Farragut's immortal 'Damn the torpedoes' figured centrally within. Initially there was some reluctance to admit what had happened, or even to warn the Iowa. As the awful reality sunk in, people began racing around, shouting conflicting instructions and attempting to warn the flagship of imminent danger. First, there was a flashing light warning about the torpedo which unfortunately indicated it was headed in another direction. Next, the Porter signaled that it was going reverse at full speed! Finally, they decided to break the strictly enforced radio silence. The radio operator on the destroyer transmitted "'Lion (code for the Iowa), Lion, come right." The Iowa operator, more concerned about radio procedure, requested that the offending station identify itself first. Finally, the message was received and the Iowa began turning to avoid the speeding torpedo.
Meanwhile, on the Iowa's bridge, word of the torpedo firing had reached FDR, who asked that his wheelchair be moved to the railing so he could see better what was coming his way. His loyal Secret Service guard immediately drew his pistol as if he was going to shoot the torpedo. As the Iowa began evasive maneuvers, all of her guns were trained on the William D Porter. There was now some thought that the Porter was part of an assassination plot. Within moments of the warning, there was a tremendous explosion just behind the battleship. The torpedo had been detonated by the wash kicked up by the battleship's increased speed.
The crisis was over and so was Captain Walker's career. His final utterance to the Iowa, in response to a question about the origin of the torpedo, was a weak, "We did it." Shortly thereafter, the brand new destroyer, her Captain and the entire crew were placed under arrest and sent to Bermuda for trial. It was the first time that a complete ship's company had been arrested in the history of the US Navy. The ship was surrounded by Marines when it docked in Bermuda, and held there several days as the closed session inquiry attempted to determine what had happened. Torpedoman Dawson eventually confessed to having inadvertently left the primer in the torpedo tube, which caused the launching. Dawson had thrown the used primer over the side to conceal his mistake. The whole incident was chalked up to an unfortunate set of circumstances and placed under a cloak of secrecy. Someone had to be punished. Captain Walker and several other Porter officers and sailors eventually found themselves in obscure shore assignments. Dawson was sentenced to 14 years hard labor. President Roosevelt intervened; however, asking that no punishment be meted out for what was clearly an accident. The destroyer was banished to the upper Aleutians. It was probably thought this was as safe a place as any for the ship and anyone who came near her. She remained in the frozen north for almost a year, until late 1944, when she was re-assigned to the Western Pacific.
Before leaving the Aleutians, she accidentally left her calling card in the form of a five-inch shell fired into the front yard of the American base commandant, thus rearranging his flower garden. In December, 1944, she joined the Philippine invasion forces and acquitted herself quite well. She distinguished herself by shooting down a number of attacking Japanese aircraft. Regrettably, after the war, it was reported that she also shot down three American planes. This was a common event on ships, as many gunners, fearful of kamikazes, had nervous trigger fingers.
In April, 1945, the destroyer was assigned to support the invasion of Okinawa. By this time, the greeting "Don't Shoot, We're Republicans" was commonplace and the crew of the Willie D had become used to the ribbing. But the crew of her sister ship, the USS Luce, was not so polite in its salutations after the Porter accidentally riddled her side and superstructure with gunfire.
On 10 June, 1945, the Porter's hard luck finally ran out. She was sunk by a plane which had (unintentionally) attacked underwater. A Japanese bomber made almost entirely of wood and canvas slipped through the Navy's defense. Having little in the way of metal surfaces, the plane didn't register on radar. A fully loaded kamikaze, it was headed for a ship near the Porter, but just at the last moment veered away and crashed along side the unlucky destroyer. There was a sigh of relief as the plane sunk out of sight, but then it blew up underneath the Porter, opening her hull in the worst possible location.
Three hours later, after the last man was off board, the Captain jumped to the safety of a rescue vessel and the ship that almost changed world history slipped astern into 2,400 feet of water. Not a single soul was lost in the sinking. After everything else that happened, it was almost as if the ship decided to let her crew off at the end.
All photographs copyright Scott Nickell Photography and may not be used without the photographer's written consent.
| comment | |